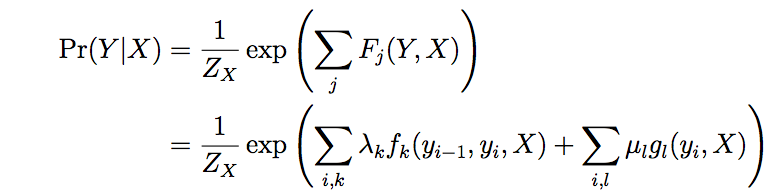Incorporating Conditional Random Fields (CRF) and Active Learning to Improve Sentiment Identification
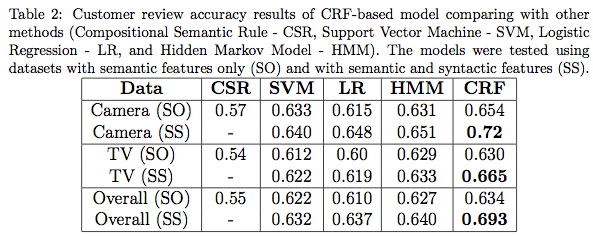
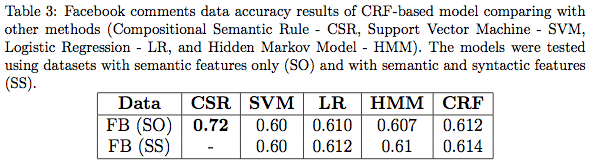
Many machine learning, statistical, and computational linguistic methods have been developed to identify sentiment in sentences in documents, yielding promising results. However, most of the current state-of-the-art methods focus on individual sentences and ignore the impact of context on the meaning of a sentence. In this paper, we propose a method based on conditional random fields to incorporate sentence structure and context information in addition to syntactic information. We also investigate how human interaction affects the accuracy of sentiment labeling using limited training data. We propose and evaluate two different active learning strategies for labeling sentiment data.
-
Publication
35th ACM SIGIR 2012Kunpeng Zhang, Yusheng Xie, Yu Cheng, Doug Downey, Ankit Agrawal, Wei-keng Liao, and Alok Choudhary. Sentiment Identification by Incorporating Syntactics, Semantics and Context Information -
Publication
under journal reviewIncorporating Conditional Random Fields and Active Learning to Improve Sentiment Identification
- How to take full advantage of the sentence structure;
- How to use context information to capture the relationship among sentences and to improve document-level sentiment classification;
- How to account for Internet language word set and emoticons;
- How to incorporate human interaction to improve sentiment identification accuracy and construct a large training dataset.
-
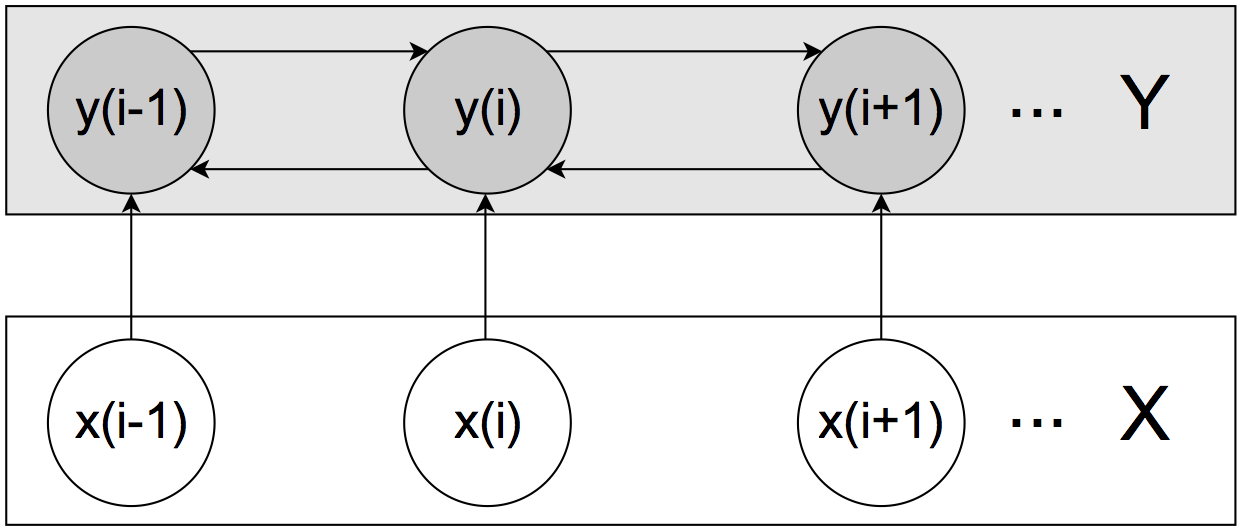
We want to capture the context information (e.g., neighboring sentences or sentences connected by transition words) among sentences in a document. The procedure of sentiment identification therefore becomes a kind of sequence labeling.
-
The goal of the model is to give a label to each sentence corresponding to the sentence sequence. We use CRF as a tool to model this sequence labeling problem.
- Number of Positive/Negative Words
- Containing Any Positive/Negative Emoticons
- Comparative Sentences (JJR vs RBR vs JJS vs RBS)
- Type of Conjunction Words (IN vs CC)
- Sentence Position in Paragraph
- Sentence/clause Complexity
- Position of Positive/Negative Words
- Position of Negation Words
- Comparison Subject
- Similarity to Neighboring Sentences
- Levenshtein
- LSI-Levenshtein
python ./prepare.pycheck the parameters, paths, etc.python ./generate_template.pyif necessary.bash ./run_crf.shmodifyrun_crf.shif necessary.
- Dataset contains long, complicated sentences from Stanford & Northwestern.
- CRF++ is a great tool.
Collaborators: @kpzhang @hixiaoxi