-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 8
Array mapping
zmjack edited this page Jun 12, 2023
·
1 revision
Map the original array to a new type array without changing the overall structure.
Example 1 ( 1d - 1d )
var d1_d1 = new string[2][]
{
new string[1] { "0" },
new string[2] { "1", "2" },
};
var result = d1_d1.Map((string s) => int.Parse(s)) as int[][];
Assert.Equal(new[] { 0, 1, 2 }, Any.Flat<int>(result));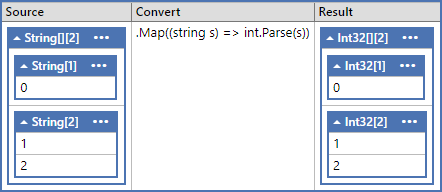
Example 2 ( 1d - 2d )
var d1_d2 = new string[2][,]
{
new string[2, 1]
{
{ "0" },
{ "1" },
},
new string[1, 2]
{
{ "2", "3" },
},
};
var result = d1_d2.Map((string s) => int.Parse(s)) as int[][,];
Assert.Equal(new[] { 0, 1, 2, 3 }, Any.Flat<int>(result));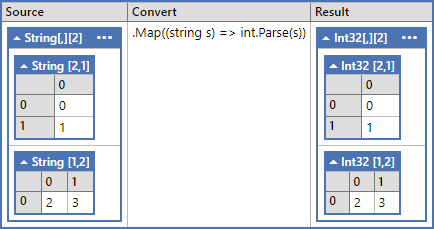
Example 3 ( 1d - 2d - 1d )
var d1_d2_d1 = new string[2][,][]
{
new string[1, 2][]
{
{
new string [1] { "0", },
new string [2] { "1", "2" },
},
},
new string[2, 1][]
{
{
new string [2] { "3", "4",},
},
{
new string [3] { "5", "6", "7"},
},
},
};
var result = d1_d2_d1.Map((string s) => int.Parse(s)) as int[][,][];
Assert.Equal(new[] { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 }, Any.Flat<int>(result));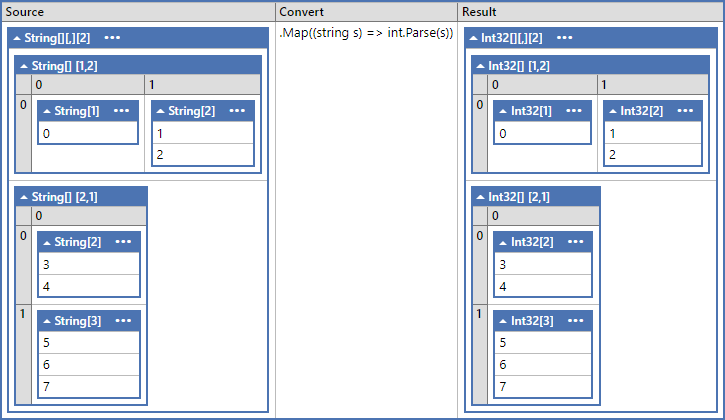
 |
 |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| English | 中文 |
- Array initialization
- Array mapping
- Array reallocation
- Chain loop
- Compose / Pipeline
- Date & Time
- Flat elements
- Index-Value Pairs
- Traverse by depth
- Zip sequences
- [Come soon] Counter
- DP container
- Evaluator
- Fixed size queue
- Scope
- Sequence input stream
- Sliding
- State
- Value with unit
- Variant string