-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 848
Add BRAVO Reader-Writer Lock #9394
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
Changes from all commits
871d2fa
f928203
94b154d
867abb7
af9914f
636d0d6
44c4047
fce0691
b494695
File filter
Filter by extension
Conversations
Jump to
Diff view
Diff view
There are no files selected for viewing
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,377 @@ | ||
| /** @file | ||
|
|
||
| Implementation of BRAVO - Biased Locking for Reader-Writer Locks | ||
|
|
||
| Dave Dice and Alex Kogan. 2019. BRAVO: Biased Locking for Reader-Writer Locks. | ||
| In Proceedings of the 2019 USENIX Annual Technical Conference (ATC). USENIX Association, Renton, WA, 315–328. | ||
|
|
||
| https://www.usenix.org/conference/atc19/presentation/dice | ||
|
|
||
| > Section 3. | ||
| > BRAVO acts as an accelerator layer, as readers can always fall back to the traditional underlying lock to gain read access. | ||
| > ... | ||
| > Write performance and the scalability of read-vs-write and write-vs-write behavior depends solely on the underlying lock. | ||
|
|
||
| This code is C++ version of puzpuzpuz/xsync's RBMutex | ||
| https://github.com/puzpuzpuz/xsync/blob/main/rbmutex.go | ||
| Copyright (c) 2021 Andrey Pechkurov | ||
|
|
||
| @section license License | ||
|
|
||
| Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one | ||
| or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file | ||
| distributed with this work for additional information | ||
| regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file | ||
| to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the | ||
| "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance | ||
| with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at | ||
|
|
||
| http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 | ||
|
|
||
| Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software | ||
| distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, | ||
| WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. | ||
| See the License for the specific language governing permissions and | ||
| limitations under the License. | ||
| */ | ||
|
|
||
| #pragma once | ||
|
|
||
| #include "DenseThreadId.h" | ||
|
|
||
| #include "tscore/Diags.h" | ||
| #include "tscore/ink_assert.h" | ||
|
|
||
| #include <array> | ||
| #include <atomic> | ||
| #include <cassert> | ||
| #include <chrono> | ||
| #include <shared_mutex> | ||
| #include <thread> | ||
|
|
||
| namespace ts::bravo | ||
| { | ||
| using time_point = std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock>; | ||
|
|
||
| #ifdef __cpp_lib_hardware_interference_size | ||
| using std::hardware_constructive_interference_size; | ||
| #else | ||
| // 64 bytes on x86-64 │ L1_CACHE_BYTES │ L1_CACHE_SHIFT │ __cacheline_aligned │ ... | ||
| constexpr std::size_t hardware_constructive_interference_size = 64; | ||
| #endif | ||
|
|
||
| /** | ||
| ts::bravo::Token | ||
|
|
||
| Token for readers. | ||
| 0 is special value that represents inital/invalid value. | ||
| */ | ||
| using Token = size_t; | ||
|
|
||
| /** | ||
| ts::bravo::shared_lock | ||
| */ | ||
| template <class Mutex> class shared_lock | ||
| { | ||
| public: | ||
| using mutex_type = Mutex; | ||
|
|
||
| shared_lock() noexcept = default; | ||
| shared_lock(Mutex &m) : _mutex(&m) { lock(); } | ||
| shared_lock(Mutex &m, std::try_to_lock_t) : _mutex(&m) { try_lock(); } | ||
| shared_lock(Mutex &m, std::defer_lock_t) noexcept : _mutex(&m) {} | ||
|
|
||
| ~shared_lock() | ||
| { | ||
| if (_owns) { | ||
| _mutex->unlock_shared(_token); | ||
| } | ||
| }; | ||
|
|
||
| //// | ||
| // Not Copyable | ||
| // | ||
| shared_lock(shared_lock const &) = delete; | ||
| shared_lock &operator=(shared_lock const &) = delete; | ||
|
|
||
| //// | ||
| // Moveable | ||
| // | ||
| shared_lock(shared_lock &&s) : _mutex(s._mutex), _token(s._token), _owns(s._owns) | ||
| { | ||
| s._mutex = nullptr; | ||
| s._token = 0; | ||
| s._owns = false; | ||
| }; | ||
|
|
||
| shared_lock & | ||
| operator=(shared_lock &&s) | ||
| { | ||
| if (_owns) { | ||
| _mutex->unlock_shared(_token); | ||
| } | ||
| _mutex = s._mutex; | ||
| _token = s._token; | ||
| _owns = s._owns; | ||
|
|
||
| s._mutex = nullptr; | ||
| s._token = 0; | ||
| s._owns = false; | ||
| }; | ||
|
|
||
| //// | ||
| // Shared locking | ||
| // | ||
| void | ||
| lock() | ||
| { | ||
| _mutex->lock_shared(_token); | ||
| _owns = true; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| bool | ||
| try_lock() | ||
| { | ||
| _owns = _mutex->try_lock_shared(_token); | ||
| return _owns; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| // not implemented yet | ||
| bool try_lock_for() = delete; | ||
| bool try_lock_until() = delete; | ||
|
|
||
| void | ||
| unlock() | ||
| { | ||
| _mutex->unlock_shared(_token); | ||
| _owns = false; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| //// | ||
| // Modifiers | ||
| // | ||
| void | ||
| swap(shared_lock &s) | ||
| { | ||
| std::swap(_mutex, s._mutex); | ||
| std::swap(_token, s._token); | ||
| std::swap(_owns, s._owns); | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| mutex_type * | ||
| release() | ||
| { | ||
| mutex_type *m = _mutex; | ||
| _mutex = nullptr; | ||
| _token = 0; | ||
| _owns = false; | ||
| return m; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| //// | ||
| // Observers | ||
| // | ||
| mutex_type * | ||
| mutex() | ||
| { | ||
| return _mutex; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| Token | ||
| token() | ||
| { | ||
| return _token; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| bool | ||
| owns_lock() | ||
| { | ||
| return _owns; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| private: | ||
| mutex_type *_mutex = nullptr; | ||
| Token _token = 0; | ||
| bool _owns = false; | ||
| }; | ||
|
|
||
| /** | ||
| ts::bravo::shared_mutex | ||
|
|
||
| You can use std::lock_guard for writers but, you can't use std::shared_lock for readers to handle ts::bravo::Token. | ||
| Use ts::bravo::shared_lock for readers. | ||
|
|
||
| Set the SLOT_SIZE larger than DenseThreadId::num_possible_values to go fast-path. | ||
| */ | ||
| template <typename T = std::shared_mutex, size_t SLOT_SIZE = 256, int SLOWDOWN_GUARD = 7> class shared_mutex_impl | ||
| { | ||
| public: | ||
| shared_mutex_impl() = default; | ||
| ~shared_mutex_impl() = default; | ||
|
|
||
| //// | ||
| // No copying or moving. | ||
| // | ||
| shared_mutex_impl(shared_mutex_impl const &) = delete; | ||
| shared_mutex_impl &operator=(shared_mutex_impl const &) = delete; | ||
|
|
||
| shared_mutex_impl(shared_mutex_impl &&) = delete; | ||
| shared_mutex_impl &operator=(shared_mutex_impl &&) = delete; | ||
|
|
||
| //// | ||
| // Exclusive locking | ||
| // | ||
| void | ||
| lock() | ||
| { | ||
| _mutex.underlying.lock(); | ||
| _revoke(); | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| bool | ||
| try_lock() | ||
| { | ||
| bool r = _mutex.underlying.try_lock(); | ||
| if (!r) { | ||
| return false; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| _revoke(); | ||
|
|
||
| return true; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| void | ||
| unlock() | ||
| { | ||
| _mutex.underlying.unlock(); | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| //// | ||
| // Shared locking | ||
| // | ||
| void | ||
| lock_shared(Token &token) | ||
| { | ||
| ink_assert(SLOT_SIZE >= DenseThreadId::num_possible_values()); | ||
|
|
||
| // Fast path | ||
| if (_mutex.read_bias.load(std::memory_order_acquire)) { | ||
| size_t index = DenseThreadId::self() % SLOT_SIZE; | ||
| Slot &slot = _mutex.readers[index]; | ||
| bool expect = false; | ||
| if (slot.mu.compare_exchange_strong(expect, true, std::memory_order_relaxed)) { | ||
| // recheck | ||
| if (_mutex.read_bias.load(std::memory_order_acquire)) { | ||
| token = index + 1; | ||
| return; | ||
| } else { | ||
| slot.mu.store(false, std::memory_order_relaxed); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| // Slow path | ||
| _mutex.underlying.lock_shared(); | ||
| if (_mutex.read_bias.load(std::memory_order_acquire) == false && _now() >= _mutex.inhibit_until) { | ||
| _mutex.read_bias.store(true, std::memory_order_release); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| bool | ||
| try_lock_shared(Token &token) | ||
| { | ||
| ink_assert(SLOT_SIZE >= DenseThreadId::num_possible_values()); | ||
|
|
||
| // Fast path | ||
| if (_mutex.read_bias.load(std::memory_order_acquire)) { | ||
| size_t index = DenseThreadId::self() % SLOT_SIZE; | ||
| Slot &slot = _mutex.readers[index]; | ||
| bool expect = false; | ||
|
|
||
| if (slot.mu.compare_exchange_weak(expect, true, std::memory_order_release, std::memory_order_relaxed)) { | ||
| // recheck | ||
| if (_mutex.read_bias.load(std::memory_order_acquire)) { | ||
| token = index + 1; | ||
| return true; | ||
| } else { | ||
| slot.mu.store(false, std::memory_order_relaxed); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| // Slow path | ||
| bool r = _mutex.underlying.try_lock_shared(); | ||
| if (r) { | ||
| // Set RBias if the BRAVO policy allows that | ||
| if (_mutex.read_bias.load(std::memory_order_acquire) == false && _now() >= _mutex.inhibit_until) { | ||
| _mutex.read_bias.store(true, std::memory_order_release); | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| return true; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| return false; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| void | ||
| unlock_shared(const Token token) | ||
| { | ||
| if (token == 0) { | ||
| _mutex.underlying.unlock_shared(); | ||
| return; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| Slot &slot = _mutex.readers[token - 1]; | ||
| slot.mu.store(false, std::memory_order_relaxed); | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| private: | ||
| struct alignas(hardware_constructive_interference_size) Slot { | ||
| std::atomic<bool> mu = false; | ||
| }; | ||
|
|
||
| struct Mutex { | ||
| std::atomic<bool> read_bias = false; | ||
| std::array<Slot, SLOT_SIZE> readers = {}; | ||
|
Comment on lines
+334
to
+336
Collaborator
There was a problem hiding this comment. Choose a reason for hiding this commentThe reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more. It seems unlike the original BRAVO where a global reader table is used, your implementation has a reader table per lock instance. This will increase the per-lock memory footprint, with potential performance benefit. May benchmark the memory usage as well to see whether the trade-off is worthwhile/acceptable.
Contributor
Author
There was a problem hiding this comment. Choose a reason for hiding this commentThe reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more. Right, I followed the approach of xsync's RBMutex. https://github.com/puzpuzpuz/xsync/blob/main/rbmutex.go |
||
| time_point inhibit_until{}; | ||
| T underlying; | ||
| }; | ||
|
|
||
| time_point | ||
| _now() | ||
| { | ||
| return std::chrono::system_clock::now(); | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| /** | ||
| Disable read bias and do revocation | ||
| */ | ||
| void | ||
| _revoke() | ||
| { | ||
| if (!_mutex.read_bias.load(std::memory_order_acquire)) { | ||
| // do nothing | ||
| return; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| _mutex.read_bias.store(false, std::memory_order_release); | ||
| time_point start = _now(); | ||
| for (size_t i = 0; i < SLOT_SIZE; ++i) { | ||
| for (int j = 0; _mutex.readers[i].mu.load(std::memory_order_relaxed); ++j) { | ||
| std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::nanoseconds(1 << j)); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| time_point n = _now(); | ||
| _mutex.inhibit_until = n + ((n - start) * SLOWDOWN_GUARD); | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| //// | ||
| // Variables | ||
| // | ||
| Mutex _mutex; | ||
| }; | ||
|
|
||
| using shared_mutex = shared_mutex_impl<>; | ||
|
|
||
| } // namespace ts::bravo | ||
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
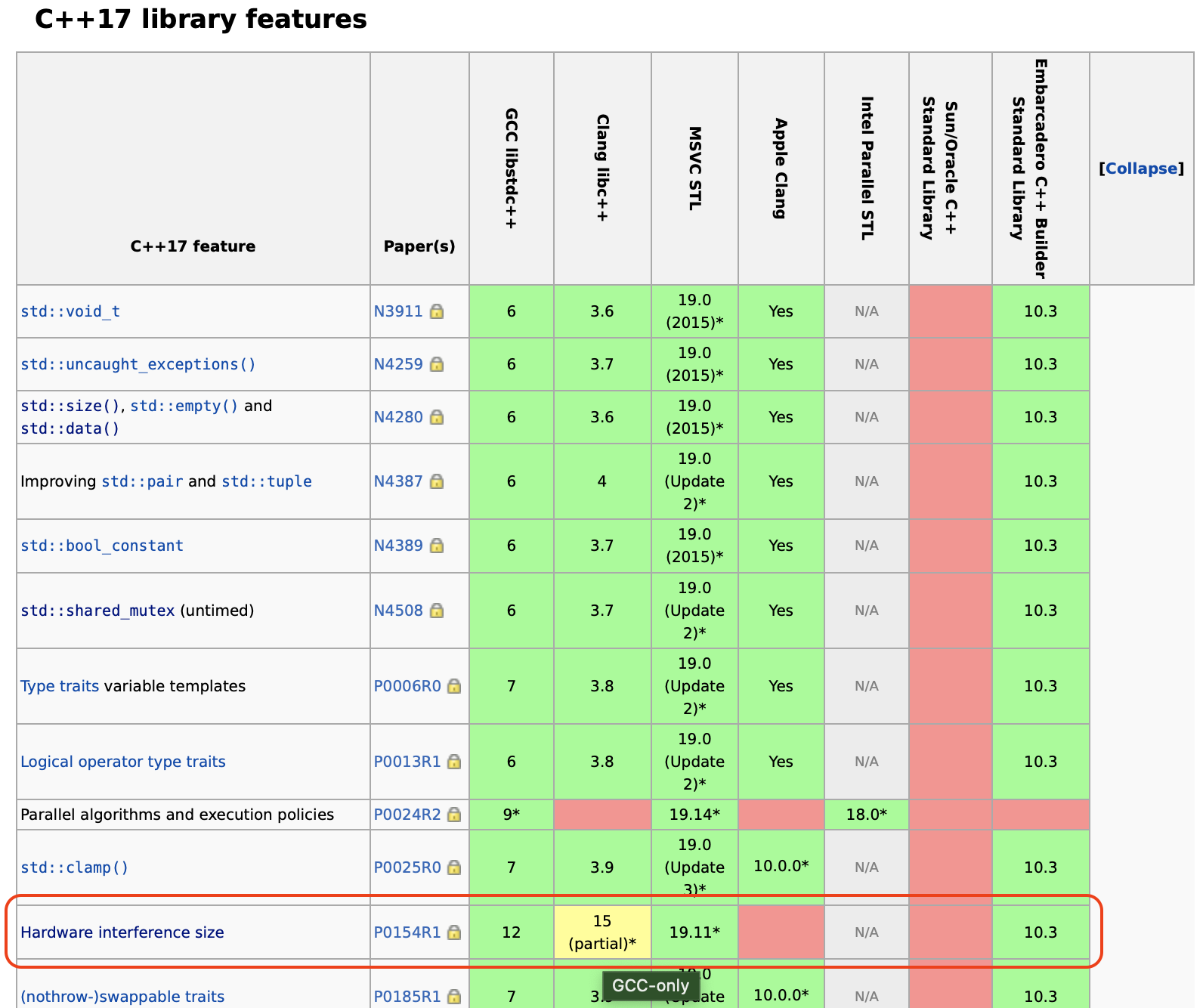
It seems like this constant is only available in newer versions of gcc and clang. We could maybe get the cache line size out of /proc/cpuinfo when the target is Linux?
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
This is C++17 but only available with GCC 😿
https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/thread/hardware_destructive_interference_size