-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 373
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
Modernize random number generator setup #1549
Conversation
RNG template class
Added ulrand to RNG class
It is replaced by Parameters
The uniform_int Parameter draws integer values from the range [0, max). Also added tests of the new Parameter.
# Conflicts: # nestkernel/rng_manager.cpp # topology/doc/source/Topology_UserManual.md # topology/doc/source/Topology_UserManual.rst
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
Thanks, looks good on my end!
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
Looks mostly good to me now, there is just a missing link that needs fixing.
Co-authored-by: Stine Brekke Vennemo <stine.vennemo@gmail.com>
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
I am happy with this now, thanks!
|
As we meanwhile have three approvals, I assume we could technically go ahead and merge this. @heplesser, @jasperalbers, @jhnnsnk, @pnbabu: speak now or forever hold your peace ;-) |
|
@jougs I would like to include the validations by @jhnnsnk and @jasperalbers properly here before merging provided all is well. @jhnnsnk and @jasperalbers, could you do the following:
I can also take care of running the tests if you provide the data. |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
I have two minor comments. Otherwise, it looks good to me.
Co-authored-by: Pooja Babu <75320801+pnbabu@users.noreply.github.com>
|
@heplesser see the data and analysis of the MAM simulations here: The plotting class also allows you to look at individual distributions, but for this somehow the bins need to be set cleverly. |
|
@jasperalbers Thank you very much! I forked your repo to https://github.com/heplesser/rng-scientific_validation and extended your script (in a rather messy way). It now plots the p-values and collects all figure for one statistical test in a single figure. I ran the Kolmogorov-Smirnov and the Epps-Singleton tests. For each of the three quantities we look at (rates, cv, cc), we have 4 x 2 x 32 tests, i.e., 256 tests. If all is well, we would thus expect about 2.5 tests to show p-values below 0.01 and 1.25 tests to show p-values below 0.005 (and correspondingly for larger p-levels). For the KS-tests this seems to be the case, for Epps-Singleton it looks like we have some more small p-values than expected. On the other hand, the expected number of p-value depends on the assumption that all values are independent, which is not really the case, since rates will be somehow correlated between populations in a simulation. A further test would be to run tests with 2.20.1 and master-rng using different random number generators to see what differences that makes. Kolmogorov-SmirnovEpps-Singleton |
|
@jasperalbers One more follow-up on my posting from last night: As a second-level test, one could collect all 256 p-values for rates (correspondingly for CV, CC) and look at their distribution. Under the null hypothesis (statistically identical results for NEST 2 and NEST 3 RNG schemes), the p-values should be uniformly distributed on [0, 1]. Knuth TAOCP vol 2 has something on this. |
|
@heplesser @jasperalbers I have now created a PR that analyzes the 4x4 data (30 runs, earlier master vs. new RNG branch) in the same way as done above for the MAM. Plots are uploaded there. Note that there is only one "area" (column). |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
Based on the validation results with the 4x4 mm² model, I approve this PR.
|
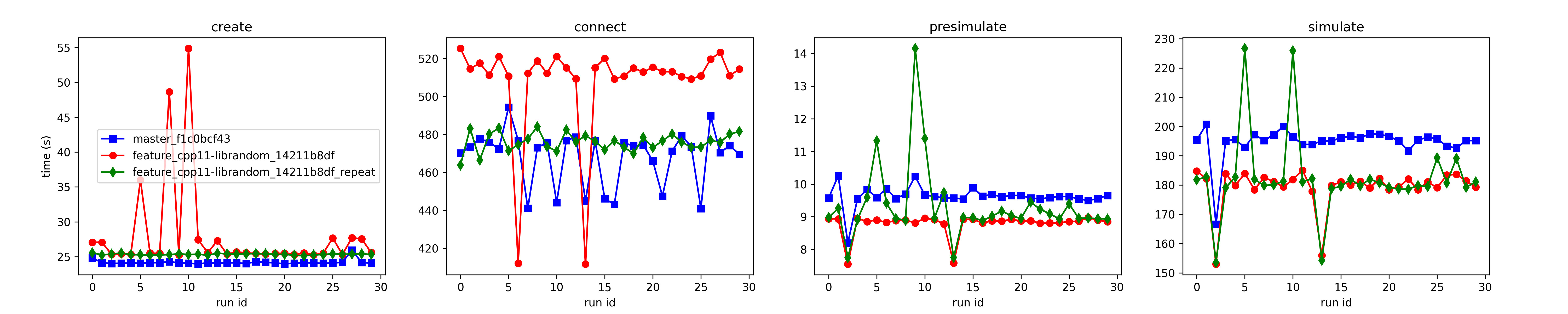
Although the statistics looks good for all runs of the 4x4 mm² model, I noticed outliers in the measured wall-clock times. Outliers may be to some extend due to the machine workload. It is not understood why the connect times of the repeated runs with the RNG-branch are rather on the level of the master branch. |
|
I have extended the statistical tests (see https://github.com/heplesser/rng-scientific_validation) to better be able to judge observed p-values for the KS and ES tests. This is in particular important since the p-values we collect from different populations within a simulation are not statistically independent from each other. To get a reference, I split the the trials we had for Old and New RNGs, respectively, into two non-overlapping groups. I then compared the two groups each to each other, separately for Old and New RNGs ("Old vs Old" and "New vs New" in figures below). This provides a reference for the distribution of p-values that might be seen in situations where differences between simulations results do not differ because of differences in RNGs used but only due to different random seeds. I then compared simulations with Old and New RNGs, for all four possible combinations of the non-overlapping trial groups ("Old vs New" in figures below). If all p-values collected had been from statistically independent data, and the null-hypothesis of each pair of samples compared were distributed according to the same underlying distribution, then p-values should be uniformly distributed on [0, 1]. Due to the correlations in our data, deviations are to be expected. The reference curves allow us to judge them. The main concern are too many small p-values (cumulative distribution functions for p-values above the diagonal), as these would indicate many cases for which the null-hypothesis of equal underlying distributions does not hold at reasonable significance levels such as 1% or 5%. CDFs are very step wise for KS and for ES for the 4x4 model due to limited number of samples, which affects KS more than ES. Figures show that Old-vs-New CDFs (brown, four per plot) generally lie not systematically above the green (Old vs Old) or blue (New vs New) reference lines. Based on this observation, I conclude that there is no indication of problems introduced by the new RNGs compared to the old, and that we can now merge the new RNGs. Thanks to @jasperalbers (MAM) and @jhnnsnk (4x4) for providing the test data! |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
Based on the scientific validation of the MAM, I approve of this PR. Thanks @heplesser for conducting the extensive statistical tests!
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
Just putting in a blocker so we can merge this in ceremonial style :).
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
All ready for the merge party now!




Overview
This PR introduces the new random number generator setup based on C++11 RNG facilities. For background, please see the discussion in #1440.
Changes for users
doublerandom numbers will have full 53-bit mantissa resolution,unsigned longrandom numbers full 64 bit range.Example
Changes for developers
KernelManager:rank_synced: same as theglobal_rngin NEST 2vp_specific: same as thethread_rngin NEST 2vp_synced: one RNG instance per VP/thread, but all need to be used in sync corresponding to the rank-synced generators; this is useful eg for the parent process inmip_generator.Issues fixed
Fixes #1440; and thus fixes #245, fixes #349, fixes #508, fixes #1296, fixes #1381, fixes #1405, fixes #1574.
Things left to do
testWithMPItestStatisticstest_activation_functiontest_lif_asctest_lif_r_asctest_lif_r_asc_atest_normal