-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 2
Filtering datasets
By clicking on the 'Filters' menu, you will obtain several option menus:
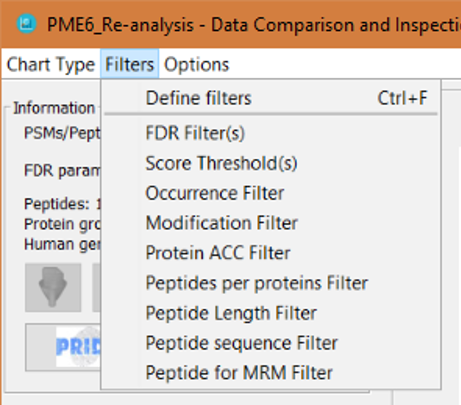
- Define filters: this will open the filters definition window
- And then, there is one option menu for each one of the available filters, which will open the filters definition window for that specific filter:
Note: Clicking on an individual filter menu when that filter was already defined, will not open the filter definition window, and it will just enable (or disable it). If the filter was not defined before, the filter definition window will open when clicking on the individual filter menu. Note 2: When a filter is active, you will see a tick mark on the individual filter menu. In order to deactivate the filter, just click again on the individual filter menu, or click on the 'Define filters' menu and click on the corresponding checkbox to disable the filter you want.
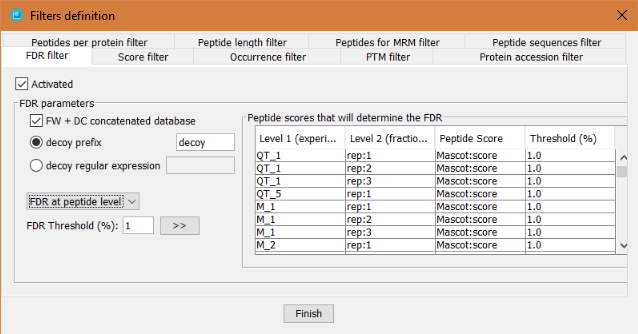
This filter will perform a False Discovery Rate (FDR) filter by calculating the FDR over a list of peptides or proteins sorted by a selected score.
Important notes about FDR in PACOM:
- The FDR is applied at level 2 of the comparison project tree.
- The FDR is applied using the peptide score, even for FDR at protein level. In case of FDR at protein level, the best peptide score for each protein is used to rank the proteins.
We are aware that this is not the most accurate way to do it, specially for protein level FDR, but due to the heterogeneity of the data that can be analyzed by PACOM, we didn't want to be stuck with a particular solution and we offer this general one. For a more accurate FDR filter, either import your data with a p-value or any other score that can be used to sort the dataset, or just import the data from an already filtered dataset.
In order to define the FDR filter, the user has to:
- Click on 'Activated' checkbox
- Define how to identify the decoy hits: by a regular expression or by a prefix.
- Define which peptide score will be taken into account to sort the peptides for level 2 nodes.
- Define which threshold will be applied. The threshold value can be different for each level 2 node.
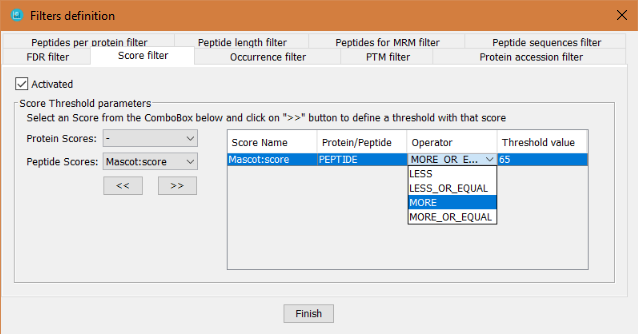
This filter defines specific threshold values applied to any score that is associated to either proteins or peptides. In order to define it, the user has to:
- Click on 'Activated' checkbox
- Select which score (peptide or protein score) will be used for the filter:
- Click on the >> button to add it to the table of score filters.
- Select the operator: LESS, LESS_OR_EQUAL, MORE or MORE_OR_EQUAL. This operator is inclusive, that is that if the selected operator is MORE, the proteins/peptides that will pass the threshold will be the ones with a score MORE than x.
- Select the threshold value and press ENTER (otherwise it is not set).
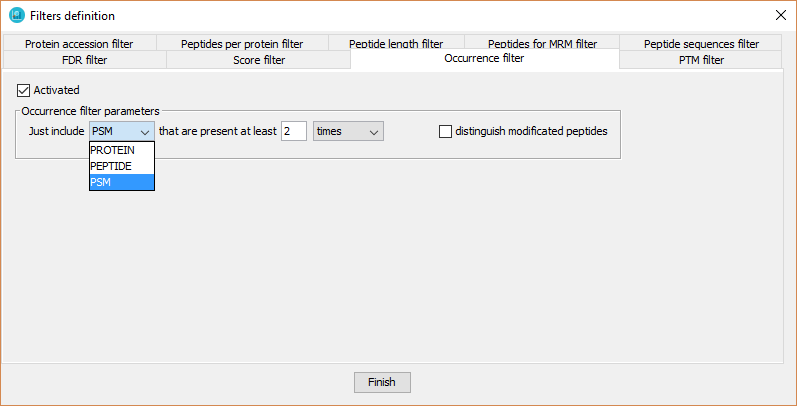
This filter will be performed just at level 1. It defines a minimum number of technical or biological replicates (sub-level 2 nodes per level 1 node) in which proteins or peptides must be detected to keep them in a dataset.
In order to define it, the user has to:
- Click on 'Activated' checkbox
- Select proteins or peptides
- Select the minimum number threshold.
- Select 'replicates' or 'times'. Selecting 'replicates' means that the protein or peptide has to be detected in at least x sub-level 2 nodes. Selecting 'times' means that the protein or peptide has to be detected x times in all the sub-level 2 nodes.
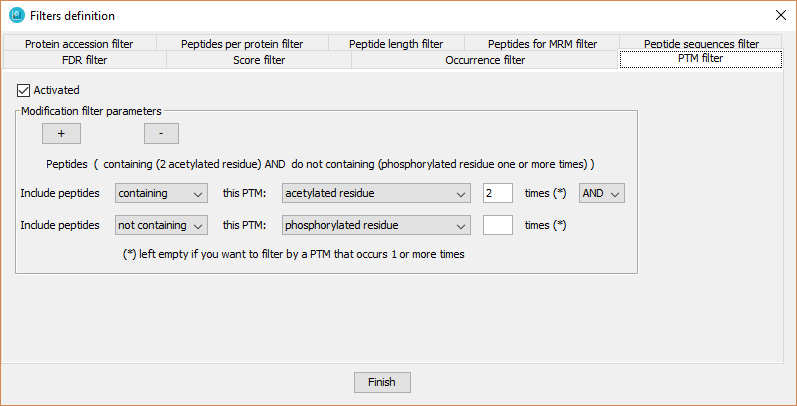
This filter defines specific peptide modifications (PTMs) and their occurrence on each peptide sequence required to keep peptides in a dataset. The user can define a logical combination of PTMs, as well as, to require to not include it (as it is shown in the previous screenshot).
In order to defined it, the user has to:
- Click on 'Activated' checkbox.
- Select 'containing' or 'non containing'.
- Select the appropriate PTM from the available PTMs detected in the current dataset.
- Select the number of PTMs that the peptides should have. It this number is left empty, the tool will select peptides containing that PTM one or more times.
- Click on ?+? button in order to include several PTM filters.
- The logical relationship between several PTM filters is defined by the logical operators ?AND? or ?OR?.
- The tool will show the resulting description of the filters in a text just above them.
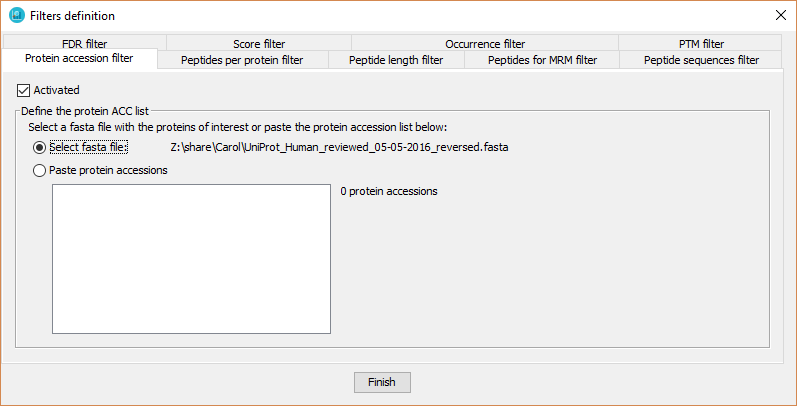
With this filter the user defines a pre-specified list of proteins in which dataset proteins must be present.
In order to define the protein acc list, the user has to:
- Click on 'Activated' checkbox
- Introduce the protein accession list:
- By selecting a fasta file containing the proteins of interest.
- By pasting a list of protein accessions (one per line).
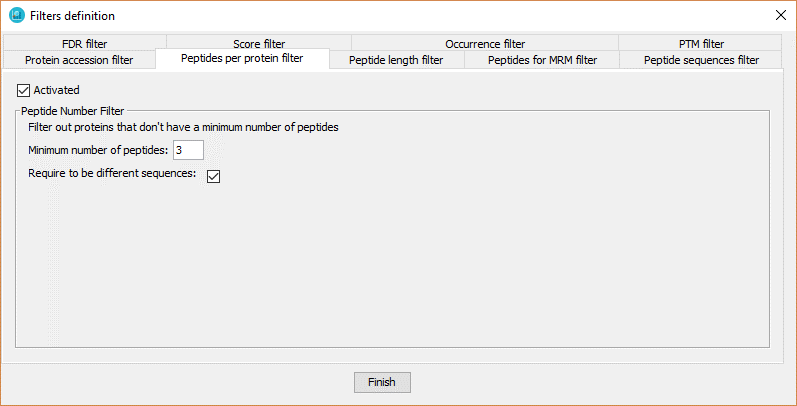
This filter defines a minimal number of peptides or PSMs per protein required to keep a protein in a dataset.
In order to define the peptide number filter, the user has to:
- Click on 'Activated' checkbox
- Introduce the number of peptides or PSMs that the proteins should have.
- Enable or not the option 'Require to be different sequences'. If disabled, the filter referes to number of PSMs per protein. If enabled, the filter refers to number of peptides per protein.
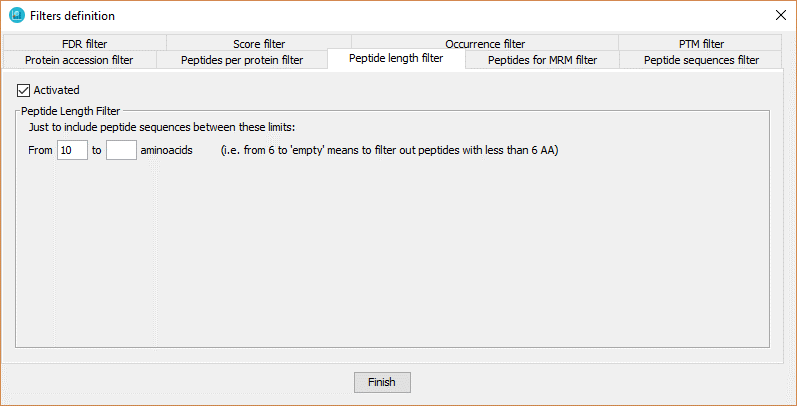
This filter defines the minimal peptide sequence length required to keep a peptide in a dataset.
In order to define the peptide number filter, the user has to:
- Click on 'Activated' checkbox.
- Introduce the range of number of aminoacid that the peptides should have. In case of selecting from x to an empty value, it means that the peptides from x aminoacid or more will be selected.
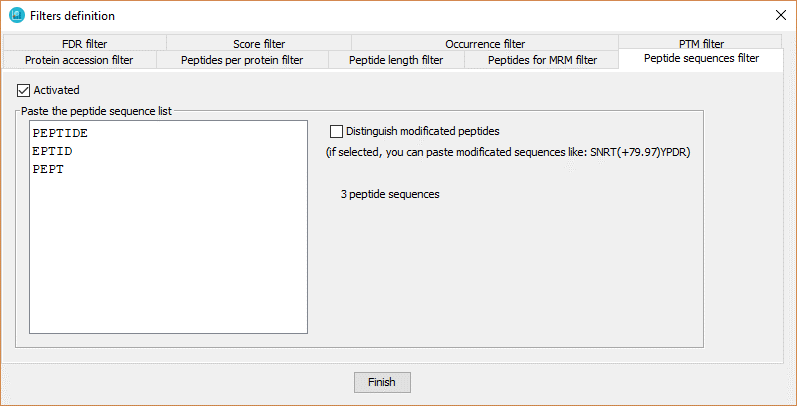
With this filter the user defines a pre-specified list of peptides in which dataset peptides must be present.
In order to define the peptide list, the user has to:
- Click on 'Activated' checkbox.
- Introduce the peptide list, one per line.
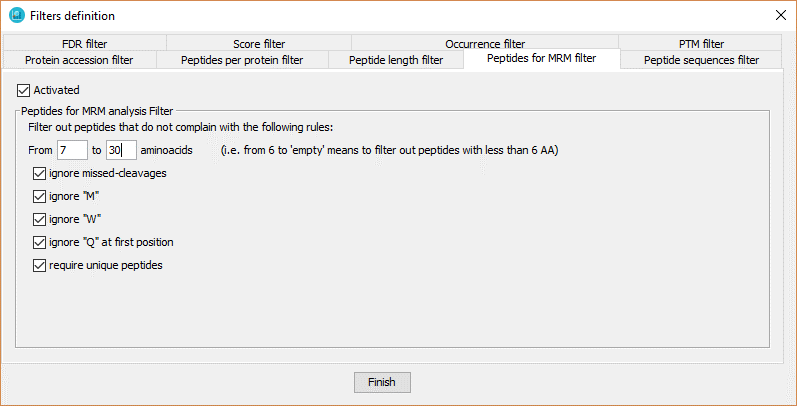
This filter selects just the peptides that have some features that make them good candidates for targeted MRM analysis, such as:
- peptides with a certain lenght.
- peptides with no missed-cleavages.
- peptides with no Methionine.
- peptides with no Tryptophan.
- peptides with no Glutamine.
- peptides not shared by multiple proteins.
In order to define the filter, the user has to:
- Click on 'Activated' checkbox.
- Select the options desired among the described above.
Contact person for any suggestion or error report:
Salvador Martínez-Bartolomé (salvador at scripps.edu)
Senior Research Associate
The Scripps Research Institute
10550 North Torrey Pines Road
La Jolla, CA 92037
Git-Hub profile