-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 2
SolarNode Logging
Logging in SolarNode is configured in the /etc/solarnode/log4j2.xml file, which is in the log4j
configuration format. The default configuration in SolarNodeOS
sets the overall verbosity to INFO and logs to a temporary storage area
/run/solarnode/log/solarnode.log.
⚠️ See the legacy logging guide for information on the older logging configuration used by SolarNode.
Log messages have the following general properties:
| Component | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Timestamp | 2022-03-15 09:05:37,029 |
The date/time the message was generated. Note the format of the timestamp depends on the logging configuration; the SolarNode default is shown in this example. |
| Level | INFO |
The severity/verbosity of the message (as determined by the developer). This is an enumeration, and from least-to-most severe: TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR. The level of a given logger allows messages with that level or higher to be logged, while lower levels are skipped. The default SolarNode configuration sets the overal level to INFO, so TRACE and DEBUG messages are not logged. |
| Logger | ModbusDatumDataSource |
A category or namespace associated with the message. Most commonly these equate to Java class names, but can be any value and is determined by the developer. Periods in the logger name act as a delimiter, forming a hierarchy that can be tuned to log at different levels. For example, given the default INFO level, configuring the net.solarnetwork.node.io.modbus logger to DEBUG would turn on debug-level logging for all loggers in the Modbus IO namespace. Note that the default SolarNode configuration logs just a fixed number of the last characters of the logger name. This can be changed in the configuration to log more (or all) of the name, as desired. |
| Message | Error reading from device. |
The message itself, determined by the developer. |
| Exception | Some messages include an exception stack trace, which shows the runtime call tree where the exception occurred. |
The Logger component outlined in the previous section allows a lot of flexibility to configure what gets logged in SolarNode. Setting the level on a given namespace impacts that namespace as well as all namespaces beneath it, meaning all other loggers that share the same namespace prefix.
For example, imagine the following two loggers exist in SolarNode:
net.solarnetwork.node.io.modbus.serial.SerialModbusNetworknet.solarnetwork.node.io.modbus.util.ModbusUtils
Given the default configuration sets the default level to INFO, we can turn in DEBUG logging for
both of these by adding a <Logger> line like the following within the <Loggers> element:
<Logger name="net.solarnetwork.node.io.modbus" level="debug"/>That turns on DEBUG for both loggers because they are both children of the net.solarnetwork.node.io.modbus namespace.
We could turn on TRACE logging for one of them like this:
<Logger name="net.solarnetwork.node.io.modbus" level="debug"/>
<Logger name="net.solarnetwork.node.io.modbus.serial" level="trace"/>That would also turn on TRACE for any other loggers in the net.solarnetwork.node.io.modbus.serial
namespace. You can limit the configuration all the way down to a full logger name if you like, for
example:
<Logger name="net.solarnetwork.node.io.modbus" level="debug"/>
<Logger name="net.solarnetwork.node.io.modbus.serial.SerialModbusNetwork" level="trace"/>The SolarNode UI supports configuring logger levels dynamically, without having to change the logging configuration file.
⚠️ When SolarNode restarts all changes made in the Logger UI will be lost and the logger configuration will revert to whatever is configured in the logging configuration file.
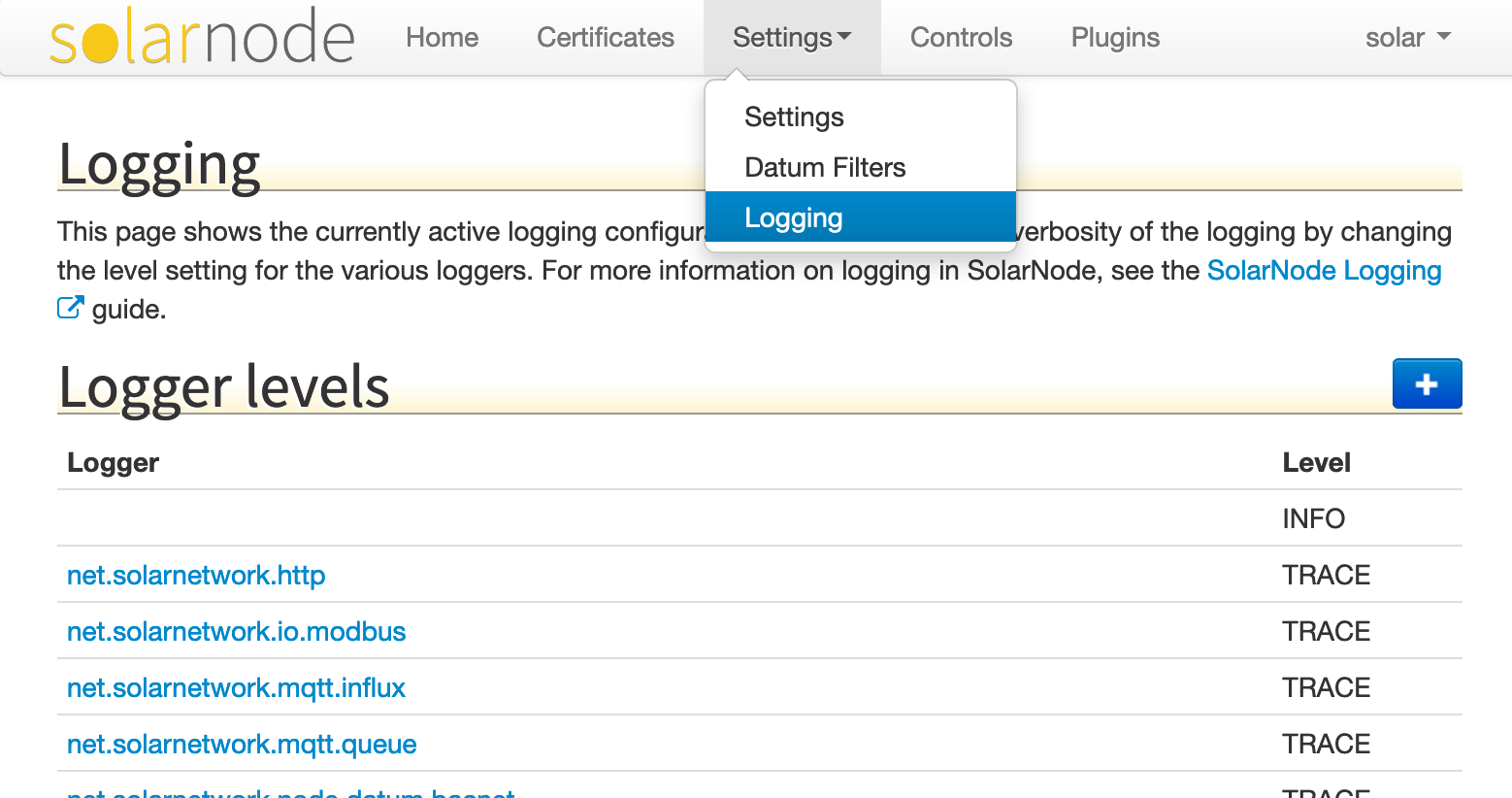
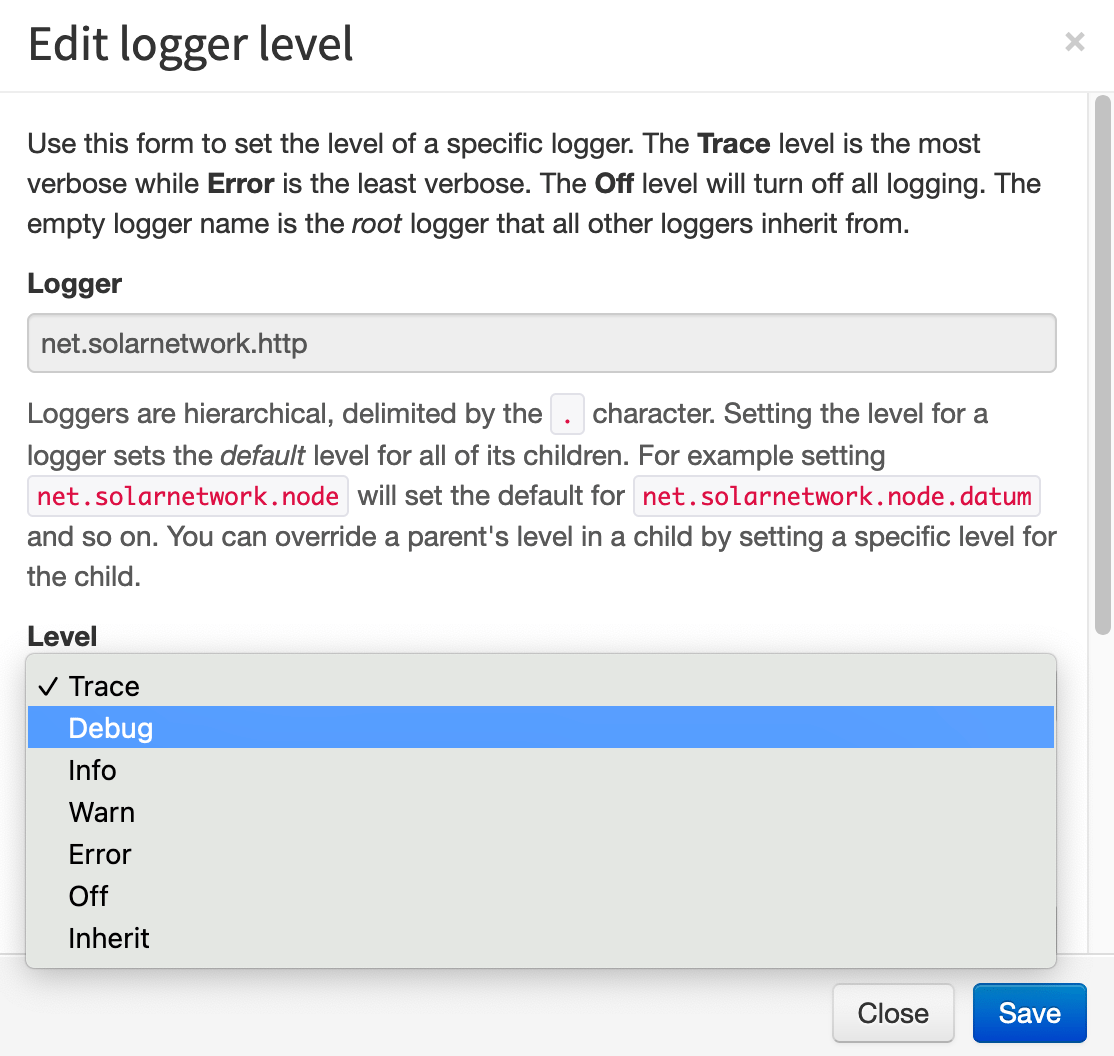
The Logging page lists all the configured logger levels and lets you add new loggers and edit the existing ones using a simple form.
The default SolarNode configuration automatically rotates log files based on size, and limits the
number of historic log files kept around, to that its associated storage space is not filled up.
When a log file reaches the file limit, it is renamed to include a -i.log suffix, where i is an
offset from the current log. The default configuration sets the maximum log size to 1 MB and
limits the number of historic files to 3.
You can also adjust how much history is saved by tweaking the <SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy> and
<DefaultRolloverStrategy> configuration. For example to change to a limit of 9 historic files of
at most 5 MB each, the configuration would look like this:
<Policies>
<SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy size="5 MB"/>
</Policies>
<DefaultRolloverStrategy max="9"/>By default SolarNode logs to temporary (RAM) storage that is discarded when the node reboots. The configuration can be changed so that logs are written directly to persistent storage if you would like to have the logs persisted across reboots, or would like to preserve more log history than can be stored in the temporary storage area.
To make this change, update the <RollingFile> element's fileName and/or filePattern attributes to point to a persistent filesystem. SolarNode already has write permission to the /var/lib/solarnode/var directory, so an
easy location to use is /var/lib/solarnode/var/log, like this:
<RollingFile name="File"
immediateFlush="false"
fileName="/var/lib/solarnode/var/log/solarnode.log"
filePattern="/var/lib/solarnode/var/log/solarnode-%i.log">
⚠️ Note that this configuration can add a lot of stress to the node's storage medium, typically an SD card. Use of this configuration should be used with caution.
Sometimes it can be useful to turn on verbose logging for some area of SolarNode, but have those
messages go to a different file so they don't clog up the main solarnode.log file. This can be
done by configuring additional appender configurations.
The following example logging configuration creates the following log files:
-
/var/log/solarnode/solarnode.log- the main log -
/var/log/solarnode/filter.log- filter logging -
/var/log/solarnode/mqtt-solarin.log- MQTT wire logging to SolarIn -
/var/log/solarnode/mqtt-solarflux.log- MQTT wire logging to SolarFlux
First you must create the /var/log/solarnode directory and give SolarNode permission to write there:
sudo mkdir /var/log/solarnode
sudo chgrp solar /var/log/solarnode
sudo chmod g+w /var/log/solarnodeThen edit the /etc/solarnode/log4j2.xml file to hold the following (adjust according to your
needs):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Configuration status="WARN">
<Appenders>
<RollingFile name="File"
immediateFlush="true"
fileName="/var/log/solarnode/solarnode.log"
filePattern="/var/log/solarnode/solarnode-%i.log">
<PatternLayout pattern="%d{DEFAULT} %-5p %40.40c; %msg%n"/>
<Policies>
<SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy size="5 MB"/>
</Policies>
<DefaultRolloverStrategy max="9"/>
</RollingFile>
<RollingFile name="Filter"
immediateFlush="false"
fileName="/var/log/solarnode/filter.log"
filePattern="/var/log/solarnode/filter-%i.log">
<PatternLayout pattern="%d{DEFAULT} %-5p %40.40c; %msg%n"/>
<Policies>
<SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy size="10 MB"/>
</Policies>
<DefaultRolloverStrategy max="9"/>
</RollingFile>
<RollingFile name="MQTT"
immediateFlush="false"
fileName="/var/log/solarnode/mqtt.log"
filePattern="/var/log/solarnode/mqtt-%i.log">
<PatternLayout pattern="%d{DEFAULT} %-5p %40.40c; %msg%n"/>
<Policies>
<SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy size="10 MB"/>
</Policies>
<DefaultRolloverStrategy max="9"/>
</RollingFile>
<RollingFile name="Flux"
immediateFlush="false"
fileName="/var/log/solarnode/flux.log"
filePattern="/var/log/solarnode/flux-%i.log">
<PatternLayout pattern="%d{DEFAULT} %-5p %40.40c; %msg%n"/>
<Policies>
<SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy size="10 MB"/>
</Policies>
<DefaultRolloverStrategy max="9"/>
</RollingFile>
</Appenders>
<Loggers>
<Logger name="org.eclipse.gemini.blueprint.blueprint.container.support" level="warn"/>
<Logger name="org.eclipse.gemini.blueprint.context.support" level="warn"/>
<Logger name="org.eclipse.gemini.blueprint.service.importer.support" level="warn"/>
<Logger name="org.springframework.beans.factory" level="warn"/>
<Logger name="net.solarnetwork.node.datum.filter" level="trace" additivity="false">
<AppenderRef ref="Filter"/>
</Logger>
<Logger name="net.solarnetwork.mqtt.queue" level="trace" additivity="false">
<AppenderRef ref="MQTT"/>
</Logger>
<Logger name="net.solarnetwork.mqtt.influx" level="trace" additivity="false">
<AppenderRef ref="Flux"/>
</Logger>
<Root level="info">
<AppenderRef ref="File"/>
</Root>
</Loggers>
</Configuration>The various <AppenderRef> set the appender name to write the messages to.
The various additivity="false" attributes disable appender additivity which means the log
message will only be written to one appender, instead of the default of being written to all
configured appenders.
The immediateFlush="false" turns on buffered logging, which means log messages are buffered in RAM
before being flushed to disk. This is more forgiving to the disk, at the expense of a delay before
the messages appear.
MQTT wire logging means the raw MQTT packets send and received over MQTT connections will be logged
in an easy-to-read but very verbose format. For the MQTT wire logging to be enabled, it must be
activated with a special configuration file. Create the
/etc/solarnode/services/net.solarnetwork.common.mqtt.netty.cfg file with this content:
wireLogging = true