-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 30
Current source density (CSD)
CSD analysis is the method used to derive the macroscopic sources and sinks that generate a potential field. Assuming that the medium is homogeneous and resistive, CSD can be approximated by a second-order derivative of the field potential.
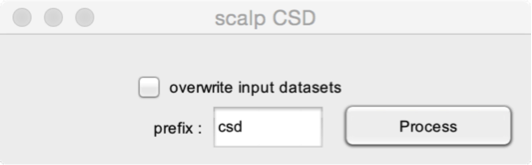
Compute Scalp CSD (spherical spline algorithm to compute scalp surface Laplacian or current source density (CSD) estimates for surface potentials. See also the CSDtoolbox website.
This function is used to compute a linear CSD.
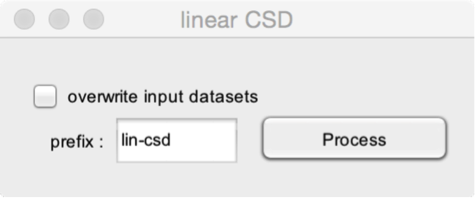
The signal of each channel is expressed as the difference between the signal at that channel and the mean of the signal measured at the two neighbouring channels. For example, the signal at channel 2 becomes the signal at channel 2 – the mean of the signals at channels 1 and 3.
Note that the first and last channels of the dataset are discarded.
Plugins
User interface
File
Edit
Events
- Browse and edit events
- Delete duplicate events
- Create events from level trigger
- Merge event codes and latencies
Pre-processing
- DC removal and linear detrend
- Reference
- Frequency filters
- Spatial filters (ICA)
- Epoch segmentation
- Baseline operations
- Artefact rejection and suppression
- Current source density (CSD)
- Frequency and time-frequency transforms
- Time-frequency filters
- Resample signals
- Resample signals
- Arrange signals
Post-processing
- Average
- Single-trial analysis
- Math
- Source analysis (dipole fitting)
- Find peaks in waveforms
- Global explained variance
Statistics
- Compare datasets against a constant
- Compare two datasets
- Compare more than two datasets (ANOVA)
- Compare signal amplitude at event latencies
- Bootstrap test against a reference interval
Figures