-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 30
Letswave 6 main user interface
André Mouraux edited this page Apr 7, 2015
·
2 revisions
The Letswave main user interface is launched by typing ‘letswave’ in the Matlab command prompt.
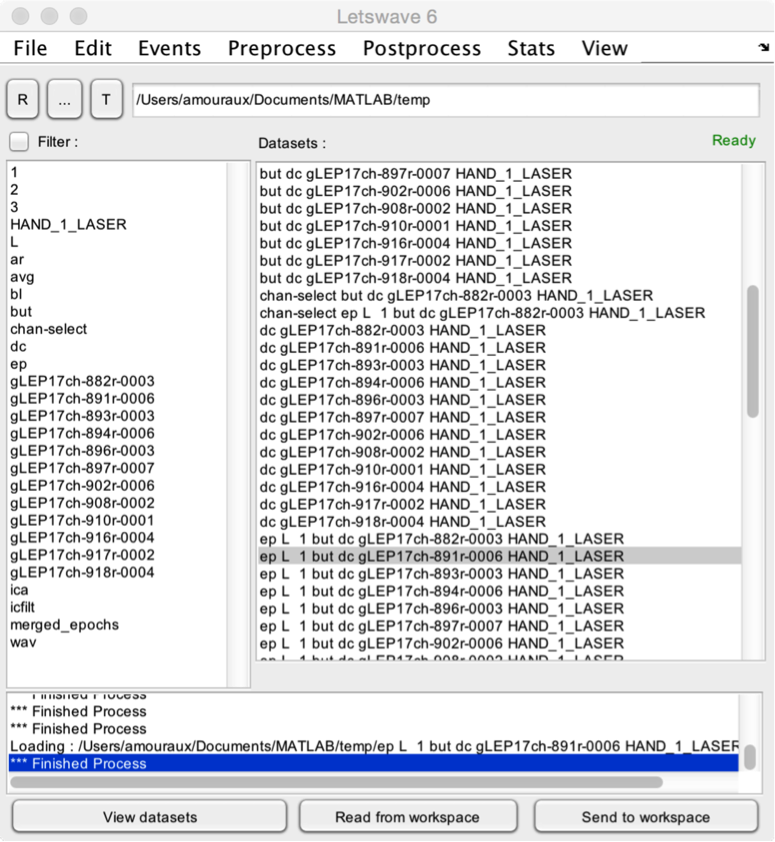
- The Datasets listbox lists all the datasets found in the current folder, sorted by alphabetical order. To apply a function to a given dataset, simply select one or more dataset(s) from that listbox, and choose the function using the dropdown title menus.
- When running a function, information regarding the process is provided in the lower text box. In addition, the upper-right Ready/Busy label provides informs whether the function is still busy processing the data, or whether it has finished.
- To view dataset(s), you can either double-click the dataset(s) in the datasets listbox, click the View datasets button, or select a custom viewer interface in the View menu.
- If you wish to modify manually a dataset using your own Matlab code, you can send dataset(s) to the Matlab workspace using the Send to workspace button. This will create a new variable in the Matlab workspace, named lwdata. The workspace variable can be imported back into Letswave using the Read from workspace button. This will replace the content of the selected dataset with the data contained in the lwdata workspace variable.
Plugins
User interface
File
Edit
Events
- Browse and edit events
- Delete duplicate events
- Create events from level trigger
- Merge event codes and latencies
Pre-processing
- DC removal and linear detrend
- Reference
- Frequency filters
- Spatial filters (ICA)
- Epoch segmentation
- Baseline operations
- Artefact rejection and suppression
- Current source density (CSD)
- Frequency and time-frequency transforms
- Time-frequency filters
- Resample signals
- Resample signals
- Arrange signals
Post-processing
- Average
- Single-trial analysis
- Math
- Source analysis (dipole fitting)
- Find peaks in waveforms
- Global explained variance
Statistics
- Compare datasets against a constant
- Compare two datasets
- Compare more than two datasets (ANOVA)
- Compare signal amplitude at event latencies
- Bootstrap test against a reference interval
Figures